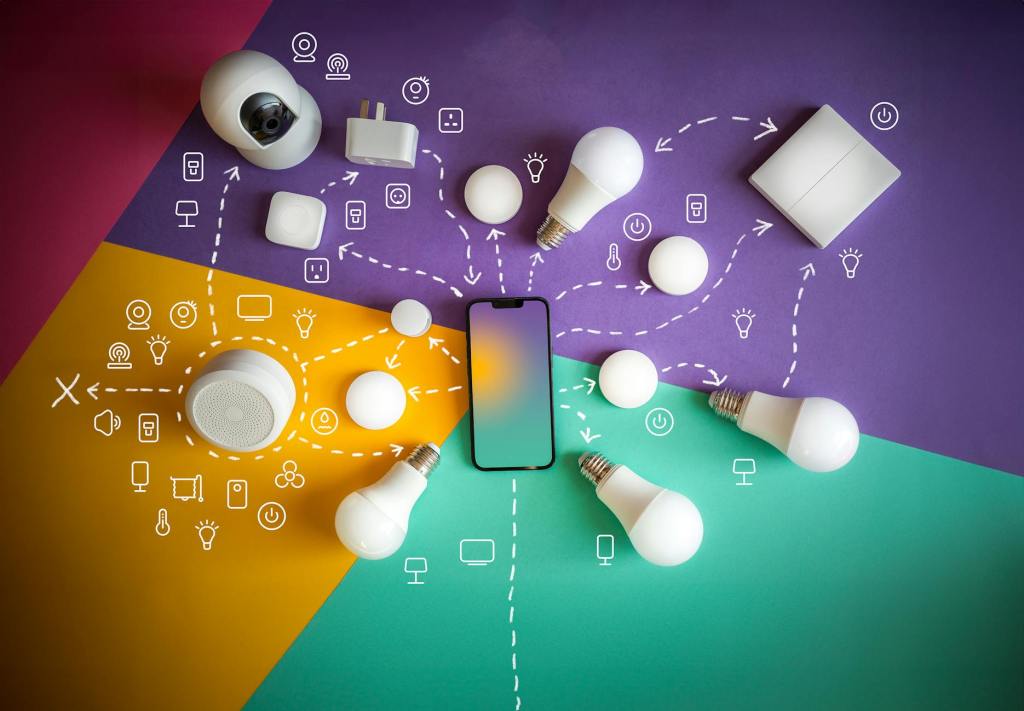
Artificial intelligence (AI) and biotechnology are both growing at breakneck speed, with the potential to enhance our lives and potentially lengthen our lives. Few people, however, have pondered how these two cutting-edge technologies may work together to address global health and environmental issues.
Let’s take a look at how quickly both professions have advanced recently. Biotechnology has improved by a factor of 10 every year in terms of cost-benefit analysis. The cost of reading the human genome has reduced from $3 billion in 2001 to under $1,000 today; what used to take months now takes less than an hour.
Biotechnology is a strange combination of two apparently unrelated domains. On the one hand, we have living organisms—wild, unpredictable celestial creations that will almost certainly never be fully comprehended or appreciated, and on the other, we have the technology—a cold, artificial entity that exists to provide convenience, structure, and mathematical certainty in human lives.
Biotechnology is an essential aspect of both healthcare and medicine, therefore the contrast works well in conjunction. There are various areas in which biotechnology plays a key role, including deep-sea research, protein synthesis, food quality management, and environmental degradation prevention.
One of the key reasons for AI’s expanding range of applications is its growing participation in biotechnology. In this blog, we will focus on AI’s applications in the field of biotechnology.

Applications of AI in Biotech Firms
When it comes to the power of Big Data and data analysis, few people think of the life sciences or biotech business. Artificial Intelligence is still strongly associated with robots and other machines.
In recent years, however, the biotech sector has used them to accomplish more than just standardized operations. It is not an exaggeration to suggest that they are working on a revolutionary precision medication that will transform healthcare.

1. AI in Agricultural Biotechnology
Agricultural biotechnology creates genetically engineered plants to boost agricultural production or give current plants new features. It includes plant breeding techniques such as tissue culture, micropropagation, and molecular breeding.
- Companies like Biogen and Genentech are now using AI and Machine Learning techniques to create and teach autonomous robots that can do key agricultural chores such as crop harvesting at a much faster rate than humans.

2. AI in Medical Biotechnology
Medical biotechnology produces medications and antibiotics from live cells for the benefit of human health. It also entails the study of DNA and genetic manipulation of cells in order to boost the creation of crucial and desirable features.
Drug development makes substantial use of artificial intelligence and machine learning. Machine Learning aids in the discovery of small compounds with therapeutic potential based on known target structures.
- Machine Learning is commonly used in illness diagnosis because it utilizes the real result to enhance diagnostic tests, i.e the more diagnostic tests done, the more accurate the findings. AI is also assisting in the reduction of the radiology and radiation therapy planning process, which saves time and improves patient care.
- Enhancing EHRs with evidence-based medications and clinical decision support systems is another area where AI and Machine Learning are showing promise. Aside from the applications listed above, these technologies are commonly employed in gene editing, radiography, customized medicine, medication management, and other fields.
- Gene editing has made it easier to change DNA sequences in live creatures, allowing for more personalized gene expression. The detection of dangerous genes and the therapy of illnesses are the two primary uses of AI in gene editing. AI is known to enhance process accuracy and produce better outcomes, reducing worries about human mistakes in gene editing.
- While gene editing has problems, AI and Machine Learning have enormous promise to improve gene editing efficiency and accuracy. This will have an impact on pharmacogenomics, neonatal genetic screening tools, agricultural improvements, and more.

- Data analysis and prediction or effect of healthcare outcomes are becoming easier thanks to digital biomarkers. The prospects to use artificial intelligence (AI), particularly machine learning, are growing exponentially as patient data is being captured digitally.
- The FDA recently approved the use of the Tiger Tech COVID Plus Monitor, the first machine learning-based COVID-19 non-diagnostic screening gadget.
- In asymptomatic adults above the age of 5, the device detects particular biomarkers that may be suggestive of SARS-CoV-2 infection, as well as other hypercoagulable diseases or hyper-inflammatory states.
3. AI in Animal Biotechnology
Molecular biology techniques are used to genetically engineer/modify animals for pharmacological, industrial, or agricultural applications.

- Animal breeding is one area where AI and machine learning models may help. Selective breeding is a widespread method in which animals with the most desired features are mated together to produce offspring with the same attributes.
- This approach is also carried out at the molecular level, where genetic features among animals are chosen and bred. Large genomic data sets are being interpreted with machine learning, and a variety of genomic sequence fragments are being annotated.
4. AI in Industrial Biotechnology
- Biopolymer replacements, inventions in fields such as car components, fuels, textiles, novel chemicals, and the manufacturing process are all part of industrial biotechnology.
- To offer efficient production and higher product quality, the IoT, Machine Learning, and AI assess machinery, forecast outages, optimize equipment, and so on.
- The ideal molecular design is created using computer-aided design and AI. Robotics and machine learning are used to nurture the strains and determine how close they are to the target chemical.
5. AI in Bioinformatics
- Bioinformatics aids in the gathering, storage, processing, dissemination, analysis, and interpretation of biochemical and biological data using mathematics, computer science, and biology methods to comprehend the biological relevance of a wide range of data. The data is arranged into huge data pools. This data must be tapped into in order to acquire valuable insights.
- AI and Machine Learning are used in DNA sequencing due to a large amount of data involved, protein classification, including the catalytic role and biological function, gene expression analysis, genome annotation (where a certain level of automation is required to identify gene locations), computer-aided drug design, and other applications.
Contributions of AI in the Biotech Field
The most intriguing use of AI and machine learning has been drug discovery. Organizations are using machine learning to develop tiny compounds that potentially provide therapeutic effects based on known target structures.
The majority of AI use-cases and emerging technologies for clinical trials appear to focus on three key applications: patient recruiting, clinical trial design, and clinical trial optimization.
- Cancer is being diagnosed using machine learning and artificial intelligence. IBM Watson Genomics, developed in collaboration with Quest Diagnostics, employs machine learning to improve cancer detection accuracy. Pathology and the identification of uncommon diseases are two more ML applications. According to new research, ML is more accurate than cardiologists at detecting heart problems.
- AI has proven to be useful in lowering the planning procedure for radiation therapy to only minutes, saving doctors many days, and increasing patient care.
- DeepMind Health is collaborating with University College London Hospital to develop machine learning calculations that will improve the precision of radiation planning by distinguishing healthy tissues from cancerous ones.
There is still a lot of research being done on how to use machine learning and predictive analysis to tailor treatment to an individual’s unique health history. If successful, this can lead to more simplified results and treatment protocols.
Currently, the focus is on guided understanding, in which physicians can use genetic data and side effects to restrict analytic options or make an educated guess about a patient’s risk. In this way, risk assessment can be done using AI in the biotech industry.
- AI systems serve as aid providers for complex activities such as creating structures for gene editing. Desktop Genetics has developed an AI-powered platform for designing CRISPR gene editing structures. From RNA selection to data analysis, their gene editing software manages the entire process.
- Evidence-based medicine and clinical decision support systems built on the machine learning platform have the potential to enhance the power of an EHR system by assisting clinicians in making educated clinical decisions based on a patient’s preferences and clinical history.
AI and digital automation may also be used to successfully handle medical records. For improved patient care, the massive volume of data can be efficiently saved, structured, and accessible.
Machine learning will automate data entry and offer a virtual assistant the ability to schedule medicine shops using a representative’s phone. AI may also assist firms and reps in consumer segmentation, which might help them target potential physicians more efficiently.

The New Role of Neurosurgeons and New Fields of Neurosurgical Research in the New Era
Since the eighteenth century, humanity has experienced 3 industrial revolutions, and now we are living in the Fourth Industrial Revolution; one represented by big data, Artificial Intelligence (AI), robots and the Internet of Things (IoT). Among the 4 industrial revolutions that the world has witnessed, I believe that it is the Fourth Industrial Revolution that will bring about the most rapid change.
Many documents and articles say that over the next 10 to 20 years half of existing jobs will disappear and many new jobs will be created.
Some have selected the medical field as the area which will see the most serious job replacement effects due to advances in smart technology such as AI and robots, and physicians and pharmacists, which are considered the most stable jobs at present, will be most affected.
In some countries, AI has competed with medical students or physicians, and the results showed, as expected, that AI exceeds the abilities of human physicians. Medical counseling AI applications are already commercially available, and perhaps in the near future, robots that can even operate on a patient with their own abilities, like those only seen in movies, may actually replace doctors. Despite the opinion that AI will eventually replace 80% of doctors; fortunately, while AI or robots can help doctors with treatment, it is still difficult to completely replace them.
However, it is clear that some roles of physicians will change in the future. That is, the doctors themselves will not disappear, instead, there will be disappearing roles. Some roles will remain, and other new roles will be created. Perhaps the role of conducting diagnoses will decrease, and the role of performing the surgery will remain for the time being. So, what will be the physician’s new role?
Every industry in the world is, after all, for mankind. Its focus is on human life and the quality of human life. Therefore, the roles of doctors, who are the most expert on human life and human science, are infinite in various industrial fields. Neurosurgeons especially should play the most important role because they are experts on the nervous system, including the brain and spine that artificial intelligence and robots should resemble.









Leave a comment